today we will talk about data communication.
Data Communications
what is data communication? it is the transfer of data or information between a source and a
receiver. The source transmits the data and the receiver receives it. The
actual generation of the information is not part of Data Communications nor is
the resulting action of the information at the receiver. Data Communication is
interested in the transfer of data, the method of transfer and the preservation
of the data during the transfer process.
MoDem (types of signal)
Modem,
device that converts between analog and digital signals. Digital signals, which
are used by computers, are made up of separate units, usually represented by a
series of 1's and 0's. Analog signals vary continuously; an example of an
analog signal is a sound wave.
Modems are
often used to enable computers to communicate with each other across telephone
lines. A modem converts the digital signals of the sending computer to analog
signals that can be transmitted through telephone lines. When the signal
reaches its destination, another modem reconstructs the original digital
signal, which is processed by the receiving computer.
To convert a
digital signal to an analog one, the modem generates a carrier wave and
modulates it according to the digital signal. The process of receiving the
analog signal and converting it back to a digital signal is called
demodulation. The word "modem" is a contraction of its two basic
functions: modulation and demodulation.
Amplitude, period, frequency
The
displacement is how far the wave vibrates / oscillates about its equilibrium
(center) position.
Amplitude
is correlated with the total energy of the system in periodic motion. Larger
amplitude = greater energy.
Period (T): the time it takes for one cycle, in
seconds.
Frequency (f): the rate, or how many cycles per
second, in Hertz (cycles per second).
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial Cable consists of 2 conductors. The inner conductor is held inside an insulator with the other conductor woven around it providing a shield. An insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor.
Coaxial Cable consists of 2 conductors. The inner conductor is held inside an insulator with the other conductor woven around it providing a shield. An insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor.
The outer
shield protects the inner conductor from outside electrical signals. The
distance between the outer conductor (shield) and inner conductor plus the type
of material used for insulating the inner conductor determine the cable
properties or impedance.
Optical Fibre
Optical Fibre consists of thin glass fibres that can carry information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum and beyond. It made of glass or plastic & transmits signals in the form of light
Advantages-
Disadvantages Optical Fibre consists of thin glass fibres that can carry information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum and beyond. It made of glass or plastic & transmits signals in the form of light
Advantages-
- Noise resistance. Light is not affected by electrical or magnetic field.
- Less signal attenuation. Transmission distance is further b4 regenerated
- Higher bandwidth. Higher data rates
- Fibre-optic cable is expecsive
- Fragility. Glass fibre is easy to broken than wire. Making it less useful for applications where handware portability is required.
Data
transmissions
 The
physical connection determines how many bits (1's or 0's) can be transmitted at
a single instance of time. If only 1 bit of information can be transmitted over
the data transmission medium at a time then it is considered a Serial
Communication.
The
physical connection determines how many bits (1's or 0's) can be transmitted at
a single instance of time. If only 1 bit of information can be transmitted over
the data transmission medium at a time then it is considered a Serial
Communication.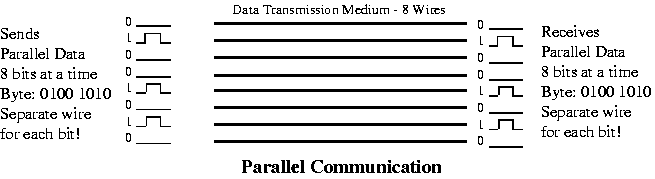 If more
than 1 bit of information is transmitted over the data transmission medium at a
time then it is considered a Parallel Communication.
If more
than 1 bit of information is transmitted over the data transmission medium at a
time then it is considered a Parallel Communication.
Data Flow
Data flow
is the flow of data between 2 points. The direction of the data flow can be
described as:
Simplex: data flows in only one direction
on the data communication line (medium). Examples are Radio and Television
broadcasts. They go from the TV station to your home television.
Half-Duplex: data flows in both directions but
only one direction at a time on the data communication line. Ex. Conversation
on walkie-talkies is a half-duplex data flow. Each person takes turns talking.
If both talk at once - nothing occurs!
Modes of Transmitting Data
- Asynchronous Transmission sends only 1 character at a time. A character being a letter of the alphabet or number or control character. Preceding each character is a Start bit and ending each character is 1 or more Stop bits. For example: for every byte of data, add 1 Start Bit and 2 Stop Bits. 11 bits are required to send 8 bits! Asynchronous is used in slow transfer rates typically up to 56 kbps.
- Synchronous Transmission sends packets of characters at a time. Each packet is preceded by a Start Frame which is used to tell the receiving station that a new packet of characters is arriving and to synchronize the receiving station's internal clock. The packets also have End Frames to indicate the end of the packet. The packet can contain up to 64,000 bits. Both Start and End Frames have a special bit sequence that the receiving station recognizes to indicate the start and end of a packet. The Start and End frames may be only 2 bytes each
Multiplexing
Multiplexing is the transmission of multiple
data communication sessions over a common wire or medium. Multiplexing reduces
the number of wires or cable required to connect multiple sessions. A session
is considered to be data communication between two devices: computer to
computer, terminal to computer,for further information, you can also view this website





5 comments:
huuuuuu...gambar membuatkan saya dah cukup paham...tq ya...:)
haha....thx...
yalor! clear enough!! i want search more pics when i free..
feel want to copy ur notes la..can ar???hahaha..nice blog n of coz ur notes..gud job la sermui..baek punya puji ni nanti u kena blanja i mcD lorh...hahahah..XD
ursula.....u are so so so busy!! no time for u to search pics loo
sarah...haha, wanna copy???sure can!!! tolak markah je...hahaha....
Post a Comment